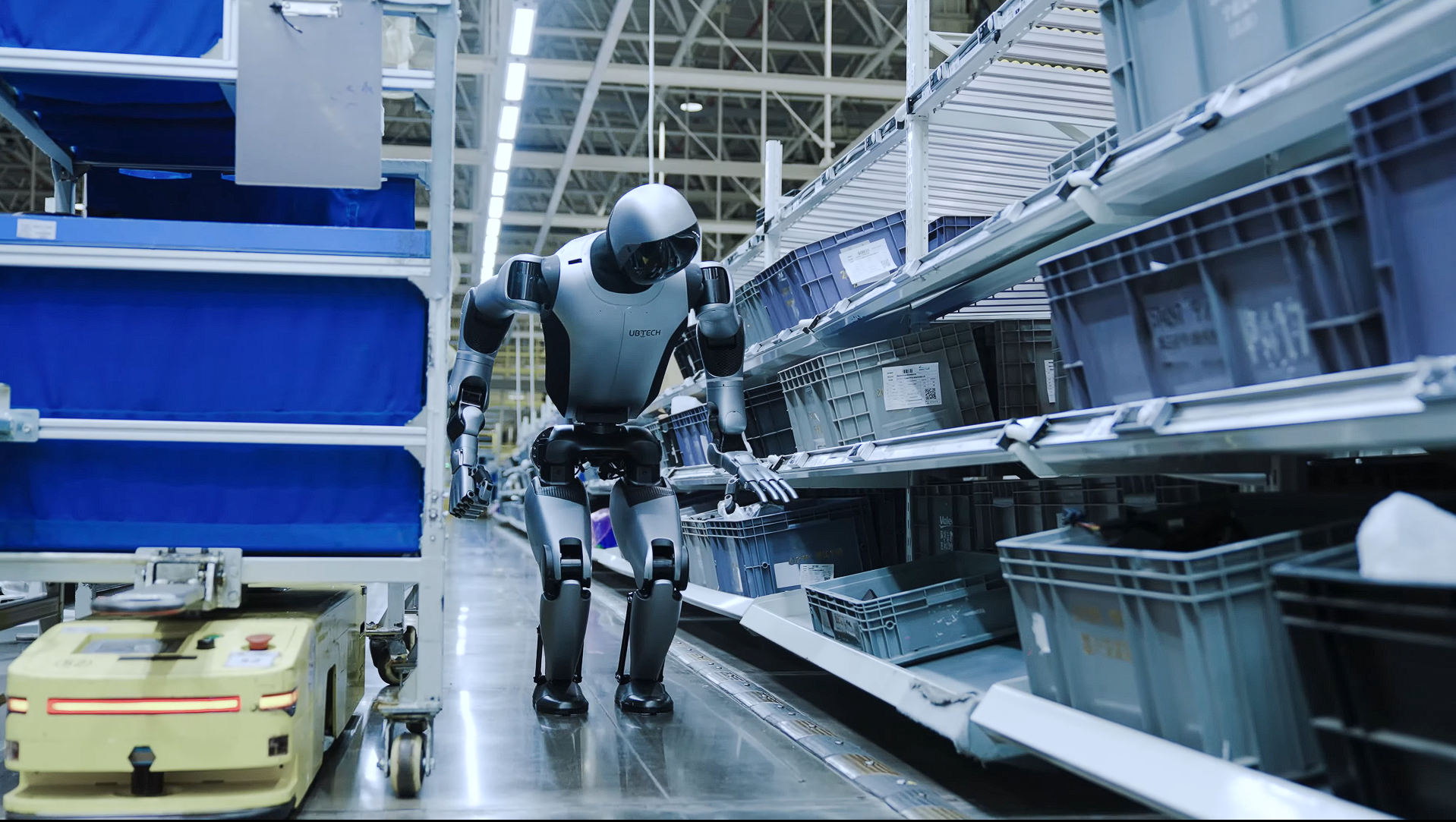
How Amazon robots continuously get smarter
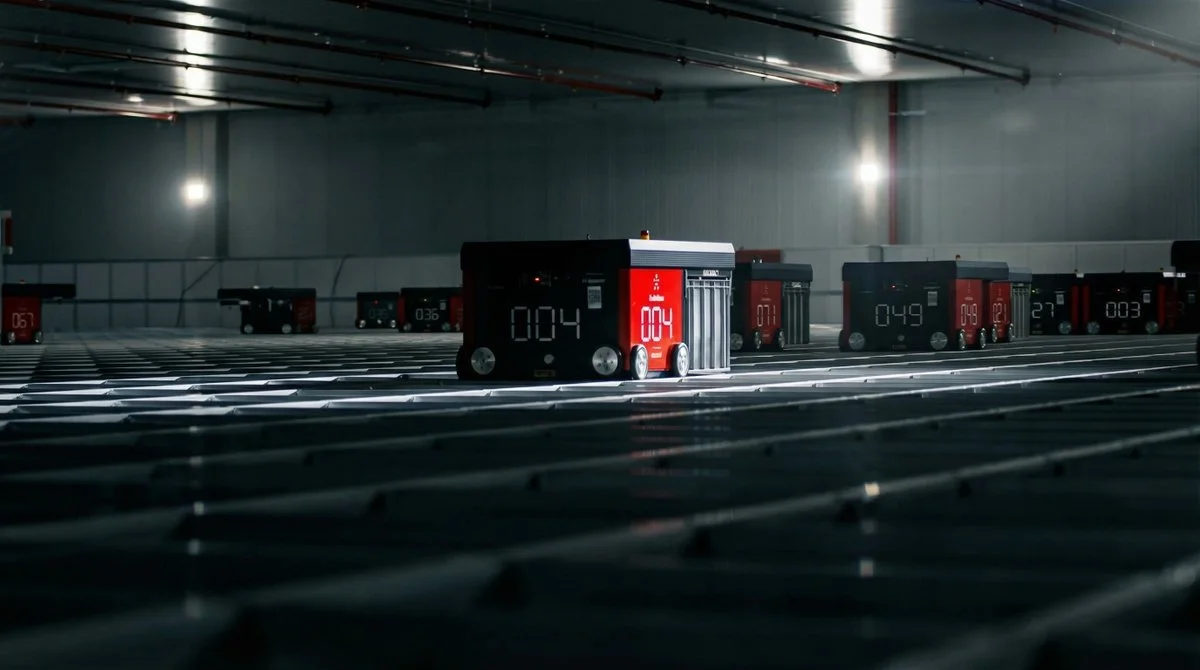
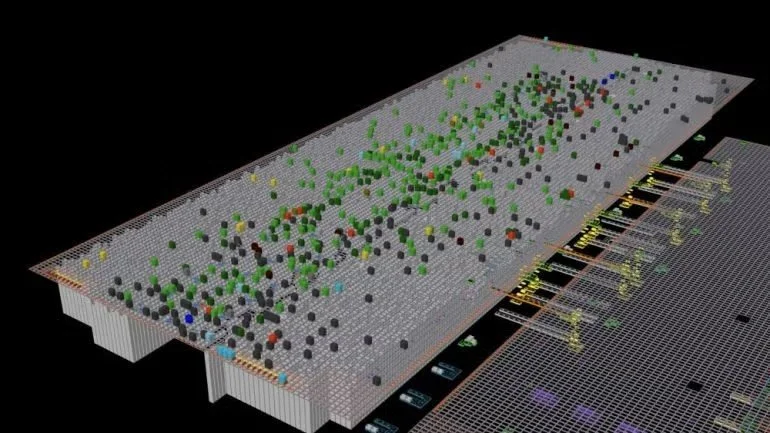
More than 3,000 robots navigate the four-story fulfillment center in Kent, guided by new algorithms that are making them faster and more efficient.
The robots inside Amazon's Kent Fulfillment Center are getting smarter — and the company is pressing forward with new technology that is raising familiar questions about the future of work.
More than 3,000 robots navigate the four-story building on 64th Avenue South, guided by new algorithms that are making them faster and more efficient.
"It's always going to get better, like especially with AI now," said Manny Thompson, an amnesty technician at the facility.
Earlier this year, Amazon announced it would eliminate 16,000 corporate positions to streamline operations and free up money for AI investments, on top of 14,000 corporate layoffs last fall. Meanwhile, the machinery inside facilities like Kent keeps evolving.
Robot technology has been part of the fulfillment center's operation for more than a decade. But, according to senior operations manager Antonella Godoy, what's changing are the brains behind the bots.
"We have been improving as we go, as new technology comes out," Godoy said.
New algorithms are constantly upgrading how the mobile robots move — sharpening their speed, efficiency and ability to avoid obstacles. The Roomba-like machines follow QR codes on the warehouse floor like coordinates on a map, ferrying packages through the building around the clock.
Safety features keep humans and robots working in close proximity. When Thompson walks near the machines, his solid green vest signals them to stop.
"As you can see, the drives behind me are not moving because I'm right here," he said.
The robots raise a question Amazon has faced before, are the machines replacing jobs, or reshaping them? In Thompson's case, his role as an amnesty technician exists specifically because of the robots. His job is to keep the warehouse floor clear, so the machines never stop moving.
"Without these, I wouldn't have a job. My job is based on these," he said. "I have to make sure that these robots are always moving and nothing's blocking them."
From there, it's a fast track to customers' doorsteps. At the Kent fulfillment center, humans remain a critical part of the operation.
Ocado has delivered a cube-based automation system for McKesson Canada, representing a continued expansion of its technology beyond e-commerce grocery fulfilment.
The prominent robotics startup entered bankruptcy protection in July after raising more than $200 million dollars from investors.
Another Ocado robotic cube warehouse goes dark. Sobeys’ decision highlights how fragile large, robot-heavy fulfillment models become when growth underperforms.
Automated Fulfillment Networks Don’t Always Expand Gracefully
Gartner forecasts that fewer than 100 companies will move humanoid robots beyond proof-of-concept.
Automation alone does not deliver sustainable performance or return on investment.
AutoStore has been positioned as the most space-dense ASRS solutions available. The claim has been repeated so often that it is rarely questioned.
The German online fashion retailer said activities at the Erfurt fulfilment site will end by September 2026.
How One Black Swan Event Ends the ASRS Speed Debate
The Simulated Frontier: How Physical AI Breaks the Automation Vicious Cycle
For years, cube-based ASRS systems — most notably AutoStore — have been positioned as the most space-dense storage solutions available. The claim has been repeated so often that it is rarely questioned.
Before You Replace Your WMS, Make Sure It Can Run Unified Commerce.
AutoStore and the Assumptions Behind Centralized Grocery Fulfillment.
The Simulated Frontier: How Physical AI Breaks the Automation Vicious Cycle
UPS Buys Hundreds of Robots to Unload Trucks in Automation Push.
Zebra Technologies is winding down its autonomous mobile robot (AMR) business, built around its $290 million acquisition of Fetch Robotics in 2021.
Kroger has announced a brand-new, $391 million automated distribution center in Franklin, Kentucky.
Kroger has taken another decisive step away from the automated fulfillment strategy it launched with Ocado in 2018.
The site in Wilcza Góra was taken from groundbreaking to operational readiness in roughly a year — significantly faster than the large Ocado CFCs launched elsewhere.
Offering high performance and excellent payload capacities, these robots makes the perfect solution for a multitude of high-payload applications.
Kroger cancels plans for additional CFCs, to pay $350M to Ocado.
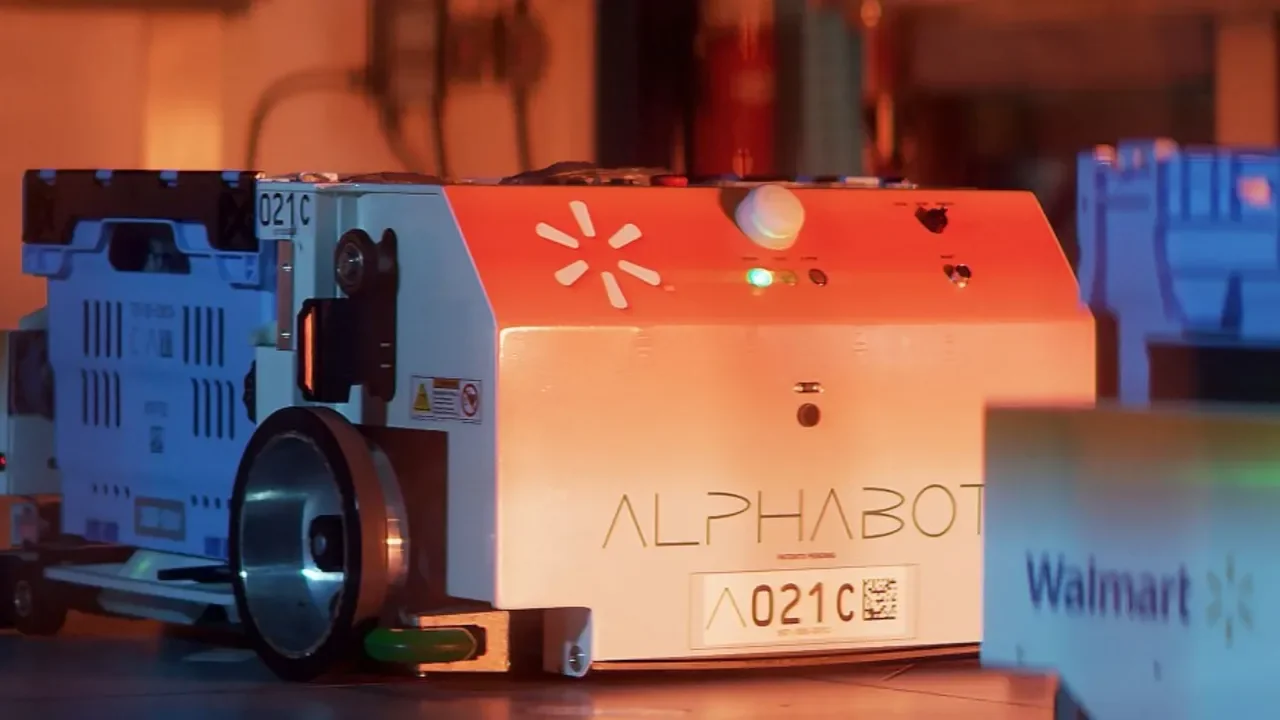
Walmart is using next-gen automation to cut a 12-step process to five and challenge Amazon on delivery speed.
Walmart’s engineers are moving away from writing every line of code and toward guiding AI-driven processes.
Watch how a full-store inventory scan can now be completed by one person in 18 minutes or less, with 100% accuracy.
Walmart’s leadership credits its momentum to one thing: using data aggressively.
The AI-supported system factors in live traffic and driver location to give customers a more accurate delivery timetable.
Why is automation underperforming? DHL’s latest data reveals the core issues.
Ocado Responds to Kroger’s CFC Closures — What Their New Statement Reveals (and What It Doesn’t).



























AutoStore reported its 2025 results this week, outlining a year that moved from early caution to clear second-half acceleration.